Stainless steel material processing-EJ Carbide Co.,Ltd
Views : 395
Update time : 2017-08-10 16:54:58
With the develop of aviation, aerospace, petroleum, chemical, metallurgical and food industries,stainless steel materials have been widely used. However, the stainless steel material has high toughness, high thermal strength, low thermal conductivity, large plastic deformation during machining, severe hardening of the work, high heat of cutting, and difficulty in heat dissipation. Therefore, the cutting temperature is high at the cutting edge, Serious mouth, easy to produce BUE, not only will aggravate the wear of the tool, but also affect the processing surface roughness. In addition, because the chip is not easy to curl and break, will damage the machined surface, affecting the quality of the workpiece.
In order to solve the above problems, EJ Carbide Co., Ltd. R & D design a series of new blade, with its excellent material, unique design, novel chip breaker shape, better solve the problems in the processing of stainless steel.
1. Stainless steel processing blade
1.1 Finishing groove type - MF
Should deal with stainless steel plastic large, strong adhesive characteristics, the design of special rake angle and blade angle groove. Blade edge sharp, cutting resistance is small, can be a good control of chip flow.
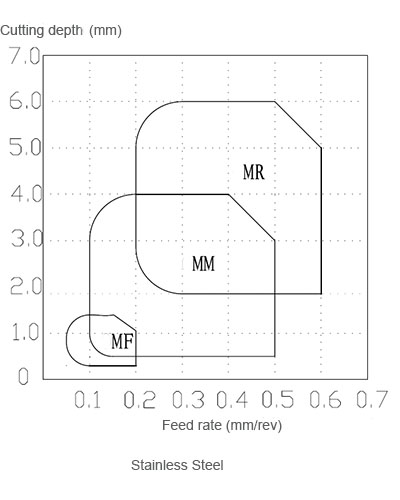
In the cutting depth of ap <1.5mm, feed fn <0.2mm / r, the iron can be in accordance with the default direction, roll into the curl along the feed in the opposite direction, will not be wrapped in the material being processed. The groove with its sharp cutting edge and lower cutting force, suitable for stainless steel finishing.
1.2 semi-finishing groove type-MM
Unique groove design in ensuring the edge of the sharp, based on the increase in the impact resistance of the blade, can effectively prevent the chip chip accumulation. When the iron scrap through the rake face, encountered flute and chip breaker, the iron will bear a certain crimp force, easy to form a small chip, so as to avoid the occurrence of winding phenomenon.

Suitable for cutting parameters with depth of cut = 0.5-4mm, feed Fn = 0.1-0.5mm / r. However, for the plastic deformation, high viscosity of the material, the groove is difficult to form a good chip, often produce winding phenomenon, and when the cutting parameters are relatively small lead to iron chip chip is not smooth. Applicable to low plastic, ordinary stainless steel semi-finished processing.
1.3 Roughing - MR
The change of the rake angle and the unique blade angle design, both to ensure the strength of the edge, but also to retain the cutting sharpness

Suitable for large cutting depth, large feed and worse conditions, the use of Ap = 2.0 ~ 6.0mm, Fn = 0.2 ~ 0.6mm / r cutting parameters have good chip breaking, especially for stainless steel Roughing and intermittent processing.
2. Chip breaking range map
3. Stainless steel processing coating grades
3.1 YBG201
High hardness of the carbide substrate, with good high temperature red hardness. Matching versatile PVD composite coating, recommended for stainless steel turning and milling.

3.2 YBG205
High hardness carbide base, with good impact resistance and excellent edge safety, with good versatility PVD coating, priority for stainless steel materials, intermittent turning and milling.

3.3 YBC251
Adopt Ti (C, N) and Al2O3 coating to achieve optimum toughness and abrasion resistance, with strong resistance to plasticity and edge strength, suitable for continuous cutting and intermittent cutting under the conditions of semi-finishing To rough processing; to achieve high-speed, efficient, environmentally friendly cutting.
In order to solve the above problems, EJ Carbide Co., Ltd. R & D design a series of new blade, with its excellent material, unique design, novel chip breaker shape, better solve the problems in the processing of stainless steel.
1. Stainless steel processing blade
1.1 Finishing groove type - MF
Should deal with stainless steel plastic large, strong adhesive characteristics, the design of special rake angle and blade angle groove. Blade edge sharp, cutting resistance is small, can be a good control of chip flow.

In the cutting depth of ap <1.5mm, feed fn <0.2mm / r, the iron can be in accordance with the default direction, roll into the curl along the feed in the opposite direction, will not be wrapped in the material being processed. The groove with its sharp cutting edge and lower cutting force, suitable for stainless steel finishing.
1.2 semi-finishing groove type-MM
Unique groove design in ensuring the edge of the sharp, based on the increase in the impact resistance of the blade, can effectively prevent the chip chip accumulation. When the iron scrap through the rake face, encountered flute and chip breaker, the iron will bear a certain crimp force, easy to form a small chip, so as to avoid the occurrence of winding phenomenon.

Suitable for cutting parameters with depth of cut = 0.5-4mm, feed Fn = 0.1-0.5mm / r. However, for the plastic deformation, high viscosity of the material, the groove is difficult to form a good chip, often produce winding phenomenon, and when the cutting parameters are relatively small lead to iron chip chip is not smooth. Applicable to low plastic, ordinary stainless steel semi-finished processing.
1.3 Roughing - MR
The change of the rake angle and the unique blade angle design, both to ensure the strength of the edge, but also to retain the cutting sharpness

Suitable for large cutting depth, large feed and worse conditions, the use of Ap = 2.0 ~ 6.0mm, Fn = 0.2 ~ 0.6mm / r cutting parameters have good chip breaking, especially for stainless steel Roughing and intermittent processing.
2. Chip breaking range map

3. Stainless steel processing coating grades
3.1 YBG201
High hardness of the carbide substrate, with good high temperature red hardness. Matching versatile PVD composite coating, recommended for stainless steel turning and milling.

3.2 YBG205
High hardness carbide base, with good impact resistance and excellent edge safety, with good versatility PVD coating, priority for stainless steel materials, intermittent turning and milling.

3.3 YBC251
Adopt Ti (C, N) and Al2O3 coating to achieve optimum toughness and abrasion resistance, with strong resistance to plasticity and edge strength, suitable for continuous cutting and intermittent cutting under the conditions of semi-finishing To rough processing; to achieve high-speed, efficient, environmentally friendly cutting.

